Medical Imaging
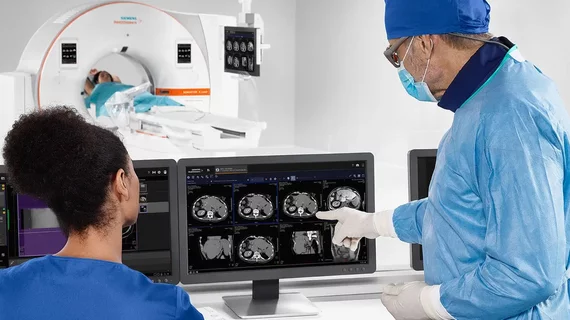
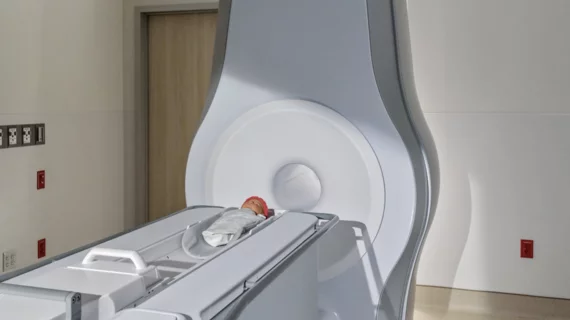
Physicians utilize medical imaging to see inside the body to diagnose and treat patients. This includes computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray, ultrasound, fluoroscopy, angiography, and the nuclear imaging modalities of PET and SPECT.
Displaying 4281 - 4288 of 5436