Computed Tomography
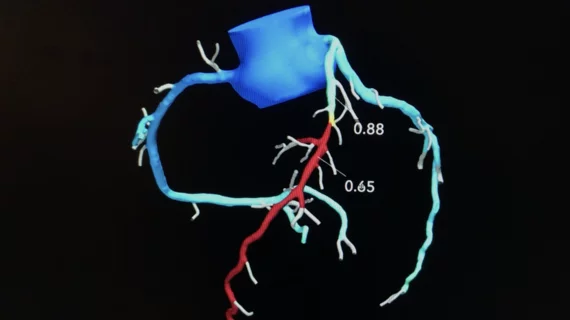
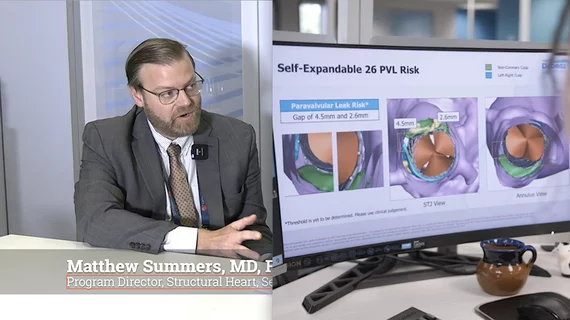
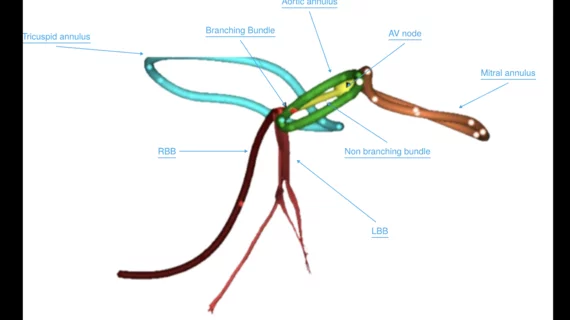
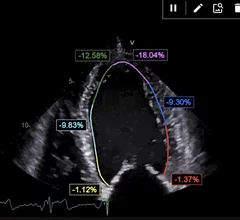
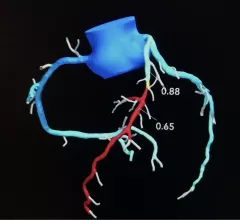
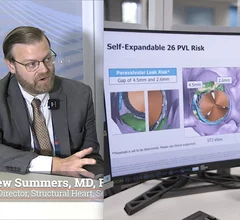
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) has become a primary cardiovascular imaging modality in the past 20 years, and was recommended as a 1A recommendation in the 2021 chest pain assessment guidelines. CT calcium scoring has became a primary risk assessment for coronary artery disease and whether patients should be on statins. Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is used to for anatomical assessment of the arteries for plaque burden and to identify areas of blockage that may cause ischemia and heart attacks. Additional use of contrast CT perfusion or fractional flow reserve CT (FFR-CT) can offer physiological information on the function of the heart. CT plays a primary role in structural heart assessments for heart valves, repair of congenital defects and left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) for both pre-procedure planning and procedural guidance. Find more news on general radiology CT use.