Enterprise Imaging
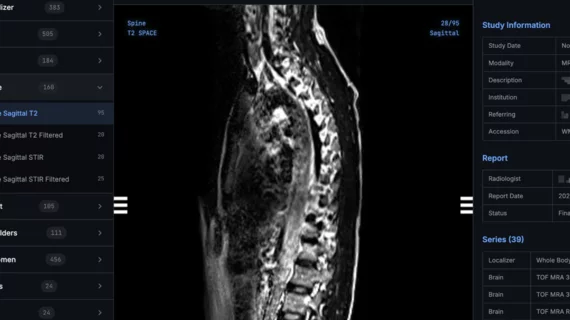
Enterprise imaging brings together all imaging exams, patient data and reports from across a healthcare system into one location to aid efficiency and economy of scale for data storage. This enables immediate access to images and reports any clinical user of the electronic medical record (EMR) across a healthcare system, regardless of location. Enterprise imaging (EI) systems replace the former system of using a variety of disparate, siloed picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), radiology information systems (RIS), and a variety of separate, dedicated workstations and logins to view or post-process different imaging modalities. Often these siloed systems cannot interoperate and cannot easily be connected. Web-based EI systems are becoming the standard across most healthcare systems to incorporate not only radiology, but also cardiology (CVIS), pathology and dozens of other departments to centralize all patient data into one cloud-based data storage and data management system.