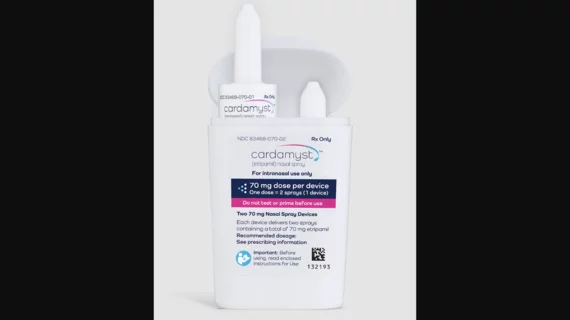
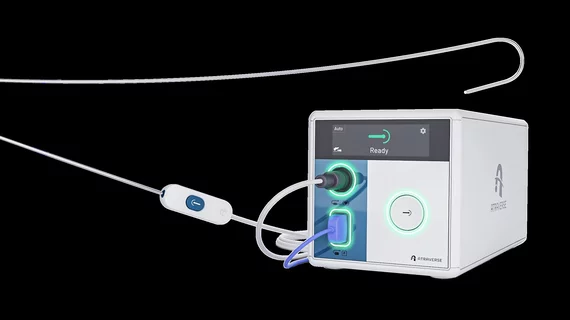
Heart Rhythm
Hearts should have normal rhythm to their beats, but when these beats are out of synch, it causes inefficient pumping of blood. Irregular heart arrhythmias occur when the electrical signals that coordinate the heart's beats do not work properly. This can cause beats that are too fast (tachycardia), or too slow (bradycardia). Tachycardias include atrial fibrillation (AFib), supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia (VT). Bradycardias include sick sinus syndrome and conduction block. Electrophysiology arrhythmia treatments include medications, life style changes, and the EP lab interventions of catheter ablation, and implantable pacemakers or defibrillators.